Flood Management
Since 2014 we have invested over £170 million in Flood Alleviation Schemes across Moray, due to its history of flooding. Floods in July 1997, November 2002 and September 2009 caused widespread damage to homes and businesses, and disruption to road and rail links.
During a flood event in August 2014, complete and partially complete flood schemes alleviated the majority of the flooding. It is estimated that the schemes have prevented damages of £86 million to date.
Flood Risk Management
The introduction of the Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act (2009), has led to a new risk-based, plan-led approach to dealing with flooding in Scotland.
Responsible authorities were designated and required to work in partnership to agree where the areas at highest risk are, set objectives, agree actions and produce a strategy and plan that would be delivered over a 6-year flood risk management planning cycle.
Individuals remain the first line of defence against flooding and are primarily responsible for their own protection. The authorities listed below have a duty to deliver a strategic, plan-led approach to managing flood risk in the Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside Local Plan District.
- The Moray Council
- The Highland Council
- Scottish Water
- Scottish Environment Protection Agency (SEPA)
- Forestry Commission Scotland
- Cairngorms National Park Authority
Flood Risk Management Strategies (FRMS)
In December 2015, SEPA published the first ever National Flood Risk Management Strategy for Scotland.
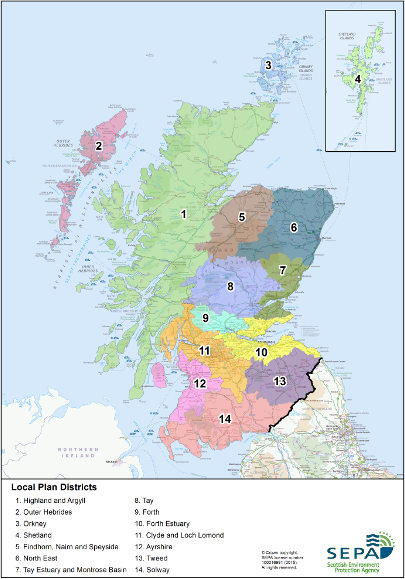
Within the Flood Risk Management Strategy, Moray communities are located in either:
- The Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside Local Plan District Area (LPD05) or
- The North East Local Plan District Area (LPD06)
The strategy describes in detail the:
- Sources and impacts of flooding within Potentially Vulnerable Areas (PVAs)
- Objectives for tackling these risks
- Appropriate actions that will then deliver these objectives and
- The prioritisation of each action in six-yearly planning cycles
SEPA Flood Risk Management Plan
Local Flood Risk Management Plans (LFRMP)
The Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act (2009) requires the lead local authority for each Local Plan District to publish a “Local Flood Risk Management Plan”.
- The Moray Council is the lead local authority for The Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside Local Plan District (LPD05), and
- Aberdeenshire Council is the lead local authority for the North East Local Plan District (LPD06)
Both local authorities have been developing Plans that will build on the Strategy, and add further detail to each action, such as:
- Funding arrangements for each action
- Which organisation will be responsible for delivery of the action
- The timescale for delivery
- Details of any coordination between authorities.
Each responsible authority has considered and approved each Plan. The Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside Local Flood Risk Management Plan can be viewed below.
Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside Local Flood Risk Management Plan Cycle 2 2022 to 2028 (PDF)
Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside Local Flood Risk Management Plan (PDF)
Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside Final Report (PDF)
The Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside Local Flood Risk Management Plan Interim Report can be viewed below.
Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside Local Flood Risk Management Plan - Interim Report
Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA)
The Moray Council, as Lead Local Authority of the Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside Local Plan District, has determined in accordance with Section 8(1) of the Environmental Assessment (Scotland) Act 2005 that a Strategic Environmental Assessment is not required for the following document:
- The Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside Local Flood Risk Management Plan
A copy of its Determination, Statement of Reasons and Screening Report can be viewed below.
Findhorn, Nairn and Speyside LFRMP SEA Screening Sea Screening Determination Statement of Reasons
The Scottish Environment Protection Agency (SEPA) have developed the animation below to show the sustainable, catchment-led approach to flooding, implemented by the Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act 2009.
